glucose is a type of hexose sugar Residual reducing sugars – vinmetrica – sulfite (so2), malic, alcohol
Biochemistry is a fascinating field that delves deep into the intricacies of living organisms at a molecular level. One of the key components of biochemistry is the study of different biomolecules, including glucose. Glucose, a simple sugar, plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes within our bodies.
Glucose - The Building Block of Life
Let’s start by understanding what glucose is. Glucose is a carbohydrate and is often referred to as the “building block of life.” It is a primary source of energy for all living organisms. In fact, glucose is the main fuel that our bodies use to carry out various functions. From providing energy to our cells to supporting brain function, glucose plays a crucial role in sustaining life.
 Research in biochemistry has shed light on multiple aspects of glucose metabolism. For instance, biochemists have discovered various pathways through which our bodies break down glucose to generate energy. These pathways, known as glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, play a fundamental role in extracting energy from glucose.
Research in biochemistry has shed light on multiple aspects of glucose metabolism. For instance, biochemists have discovered various pathways through which our bodies break down glucose to generate energy. These pathways, known as glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, play a fundamental role in extracting energy from glucose.
The Chemistry of Glucose
To understand glucose at a molecular level, it is important to take a closer look at its chemical structure. Glucose is classified as a monosaccharide, which means it is comprised of a single sugar unit. Its molecular formula is C6H12O6.
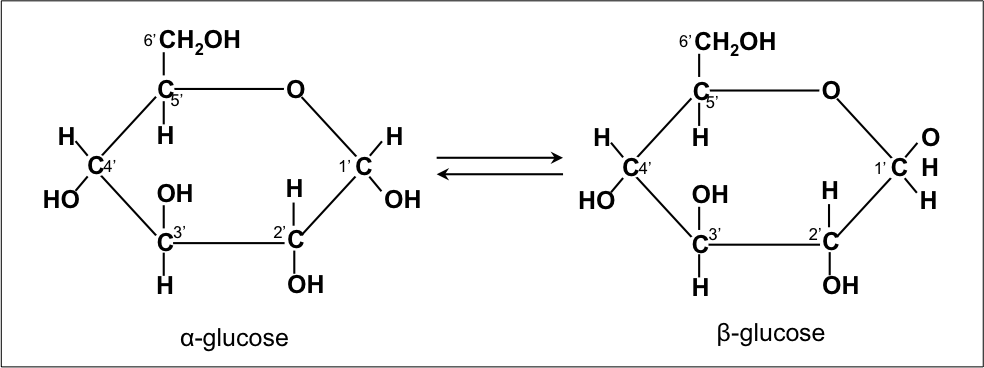
 As shown in the image above, glucose exists in two forms: alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucose. These forms differ in the orientation of the hydroxyl group attached to the carbon atom at position 1. This subtle difference gives rise to their distinct chemical properties and biological functions.
As shown in the image above, glucose exists in two forms: alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucose. These forms differ in the orientation of the hydroxyl group attached to the carbon atom at position 1. This subtle difference gives rise to their distinct chemical properties and biological functions.
The Role of Glucose in the Body
Glucose serves as a vital energy source for the human body. When we consume carbohydrates, such as bread or pasta, our digestive system breaks them down into glucose molecules. These glucose molecules are then absorbed into the bloodstream, where they are transported to our cells.
Once inside the cells, glucose undergoes a series of reactions, ultimately producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the primary energy currency of the cell. This conversion of glucose to ATP fuels the various activities of our body, including muscular contractions, nerve impulses, and protein synthesis.
In addition to energy production, glucose also plays a crucial role in maintaining the homeostasis of our body. It regulates blood sugar levels, ensuring that they remain within a narrow range. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps in this process by facilitating the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into the cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, glucose molecules are also used in the synthesis of other important biomolecules, such as nucleic acids, lipids, and certain amino acids. These molecules are essential for the proper functioning of our body and are involved in processes like DNA replication, cell membrane formation, and protein synthesis.
In conclusion, glucose, with its indispensable role in energy production and as a building block for other biomolecules, holds immense significance in biochemistry. Understanding the intricate processes involved in glucose metabolism helps us comprehend the complex workings of the human body. The findings of biochemistry research continue to deepen our knowledge of glucose and its vital role in sustaining life.
If you are looking for Pin on Biochemistry you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Pics about Pin on Biochemistry like Pin on Biochemistry, Residual Reducing Sugars – Vinmetrica – Sulfite (SO2), Malic, Alcohol and also Pin on Biochemistry. Read more:
Pin On Biochemistry
 www.pinterest.jphexose carbon
www.pinterest.jphexose carbon
Residual Reducing Sugars – Vinmetrica – Sulfite (SO2), Malic, Alcohol
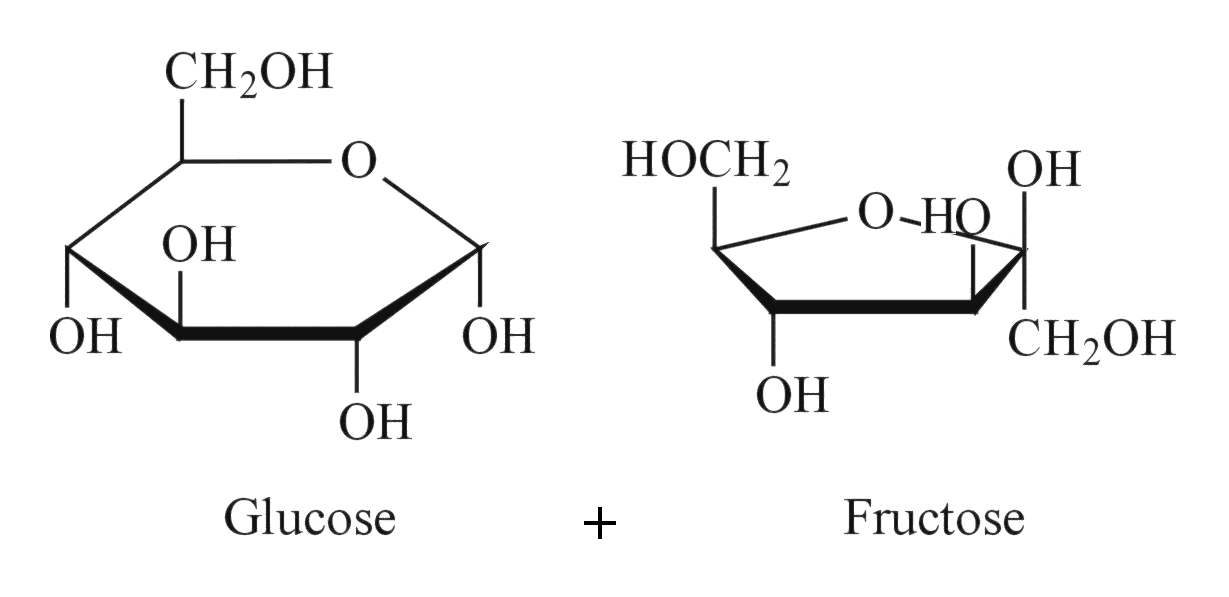 vinmetrica.comsugar sugars residual hexose reducing important why wine
vinmetrica.comsugar sugars residual hexose reducing important why wine
Carbohydrates — The Biology Primer
 thebiologyprimer.comglucose isomers monosaccharides carbohydrates
thebiologyprimer.comglucose isomers monosaccharides carbohydrates
Glucose - Wikipedia
 en.wikipedia.orgglucose glucopyranose glicose equilibrium equation interconversion alfa
en.wikipedia.orgglucose glucopyranose glicose equilibrium equation interconversion alfa
Pin On Biochemistry
 www.pinterest.comacids hexose biochemistry easybiologyclass
www.pinterest.comacids hexose biochemistry easybiologyclass
Pin on biochemistry. Sugar sugars residual hexose reducing important why wine. Acids hexose biochemistry easybiologyclass